21+ Reproductive Plant Organs
Web Plant reproductive system any of the systems sexual or asexual by which plants reproduce. Prelude to Plant Form and Physiology 302.

Reader July6 2023 By Keokee Media Marketing Issuu
Web 1 2 3 4 5 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants Sexual reproduction - plants In flowering plants male and female reproductive structures can be found in the same individual plant.
. The flowers of angiosperms and the cones of conifers clubhouses. They can be grouped into two organ systems the vegetative system and the reproductive system. The set of stamens.
Web The male gametophyte develops and reaches maturity in an immature anther. Although they are highly variable in appearance all of these organs are comprised of dermal ground and vascular tissues. Web The shoot system consisting of stems leaves and the reproductive parts of the plant.
The microsporangia which are usually bi-lobed are pollen sacs in which the microspores develop into pollen grains. The Plant Body 300. The shoot system generally grows above ground where it absorbs the light needed for photosynthesis.
Roots stems leaves flowers seeds and fruit. Reproductive organs will be covered in Chapter 5. The shoot system consists of two portions.
The first three are sometimes called the vegetative organs and are the subject of exploration in this chapter. In flowering plants the fertilization of an egg is achieved by cross- pollination. The calyx corolla androecium and gynoecium.
Web The three basic organs of vascular plants are roots stems and leaves but commonly these organs have become specialized for specific functions and do not look typical. Web A A hermaphroditic selfer. The vegetative non-reproductive parts of the plant such as the leaves and the stems and the reproductive parts of the plant which include flowers and fruits.
In a plants male reproductive organs development of pollen takes place in a structure known as the microsporangium Figure 3215 321. Web In many plant species the timing of flowering is critical for reproductive success and thus the evolution of flowering-control systems that optimize reproductive success provide a selective advantage. Light-dependent and light-independent Johnson 2016.
The most readily observed of these are stems devoted to reproductive structures. THE PLANT FLOWER Morphologically a flower is a stem tip that bears four whorls or series of specialized appendages. Sexual reproduction involves new genetic combinations and results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent plants.
Pollen is produced in the stamen. A shoot system and a root system. Sexual reproductive and vegetative.
Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are identical to the parent plant. The vegetative non-reproductive parts of the plant such as the leaves and the stems. The pollen can fertilize the ovules that are inside the same flower.
Web July 22 2021 New insight on the reproductive evolution of land plants by ITQB NOVA PI Arabidopsis thaliana. Male reproductive organs producing pollen and the second ones form the female reproductive organs bearing ovules inside closed ovaries. Web The flowering plants angiosperms go through a phase of vegetative growth producing more stems and leaves and a flowering phase where they produce the organs for sexual reproduction.
A seed contains all of. Web These structures are known as plant organs. Web There are only six plant organs.
Web Inside the flower are the reproductive organs of the plant. In annuals like the snapdragon the vegetative phase begins with germination of the seed. The pollen from the male plant needs to travel to the ovules inside the flower of the female plant in order to fertilize them.
Sexual reproduction is the sole function of flowers often the showiest part of a plant. Web Vascular plants have two distinct organ systems. Fruit consists of fertilized mature ovules seeds plus the ovary wall which may be fleshy as in an apple or.
This process involves an insect like a bee that transfers the pollen grains from the anther the male part of a flower to the stigma the female part of a flower. A shoot system and a root system. Not all flowers have every one of the four parts.
Web Reproductive morphology of plants INTRODUCTION. Vegetative parts figure 1 include roots stems shoot buds and leaves. And the reproductive parts of the plant which include flowers and fruits.
Web Vascular plants have two distinct organ systems. The shoot system consists of two portions. Web One difference between plant and animal sexual reproduction concerns fertilization.
Stems OpenStax OpenStax Skills to Develop Describe the shoot organ system and the root organ system Distinguish between meristematic tissue and permanent tissue Identify and describe the three regions where plant growth occurs. Web Plant organs include the leaf stem root and reproductive structures. Each organ is an organized group of tissues that works together to perform a specific function.
The organ systems of a typical angiosperm vascular flowering plant are illustrated below. B Outcrossing dioecious plants in which one plant has only female flowers and another has only male flowers. Around 470 million years ago plants began to conquer the.
Plants do not have nervous systems or any will for their actions. Web Reproductive plant parts Flowers. The carpel is the female reproductive organ.
The shoot system consists of two portions. Web In this section we discuss methods to assess the activity and consequences of floral organ photosynthesis directly and indirectly during plant development. The stamen is the male reproductive organ.
The ovary is the swollen base of the carpel where ovules are found. Web Vascular plants have two distinct organ systems. A shoot system and a root system.
The shoot system generally grows above ground where it. The vegetative non-reproductive parts of the plant such as the leaves and the stems and the reproductive parts of the plant which include flowers and fruits. Web Flower Structure A typical flower has four main parts or whorls.
Even so scientists are able to observe mechanisms that help their children thrive as they grow. The shoot system generally grows above ground where. Web One of the outcomes of plant reproduction is the generation of seeds spores gemmae and other vegetative organs that allow plants to move to new locations or new habitats.
Structures can be divided into two groups. There are two main reaction types during photosynthesis. The outermost whorl of the flower has green leafy structures known as sepals which are collectively called the.
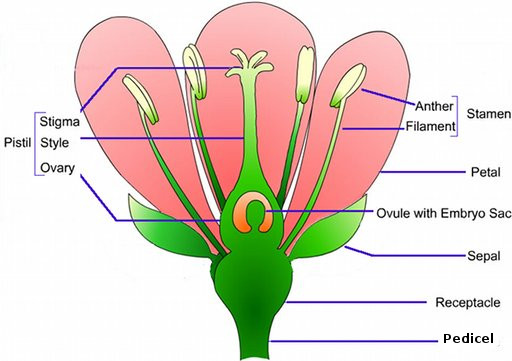
Sexual Reproduction In Plants Angiosperms Online Science Notes

Plant Reproductive System Angiosperms Pollination Fertilization Britannica

32 3 Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Sexual Reproduction In Angiosperms Biology Libretexts

Are The Reproductive Organs Of Flowering Plants

Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction In Flowering

Cannabis Plant Anatomy Explained Seed Supreme
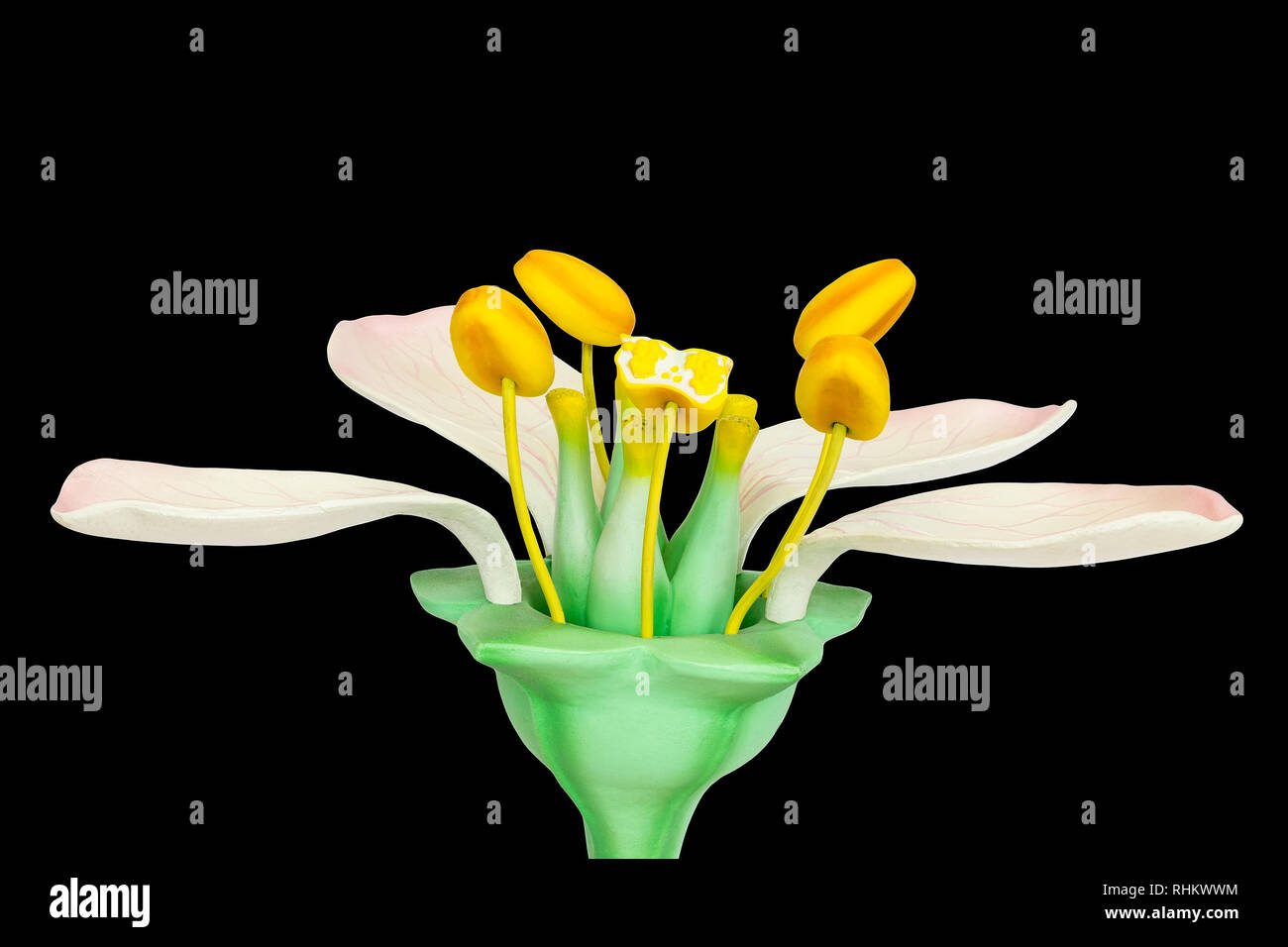

Male And Female Plant Reproductive Organs Hi Res Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Cotton Plant Development And Plant Mapping Mu Extension

Is The Reproductive Organ Of A Plant

Flowers Are The Reproductive Organs Of Plants Plant Reproductive System Youtube

Cannabis Plant Anatomy Explained Seed Supreme
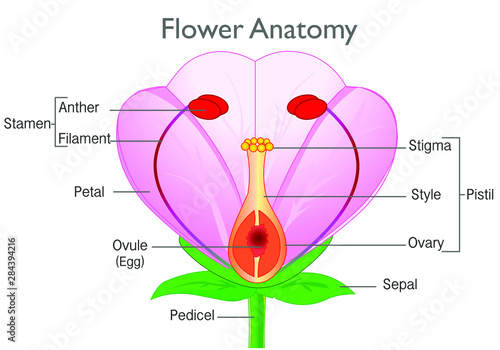
Flower Anatomy Plant Reproductive System Diagram Annotated Flowering Plants Reproduction System Pink Red Flowers Parts Components Structure White Background Drawing Illustration Vector Vector De Stock Adobe Stock
A Systematic Treatment Of Fruit Types
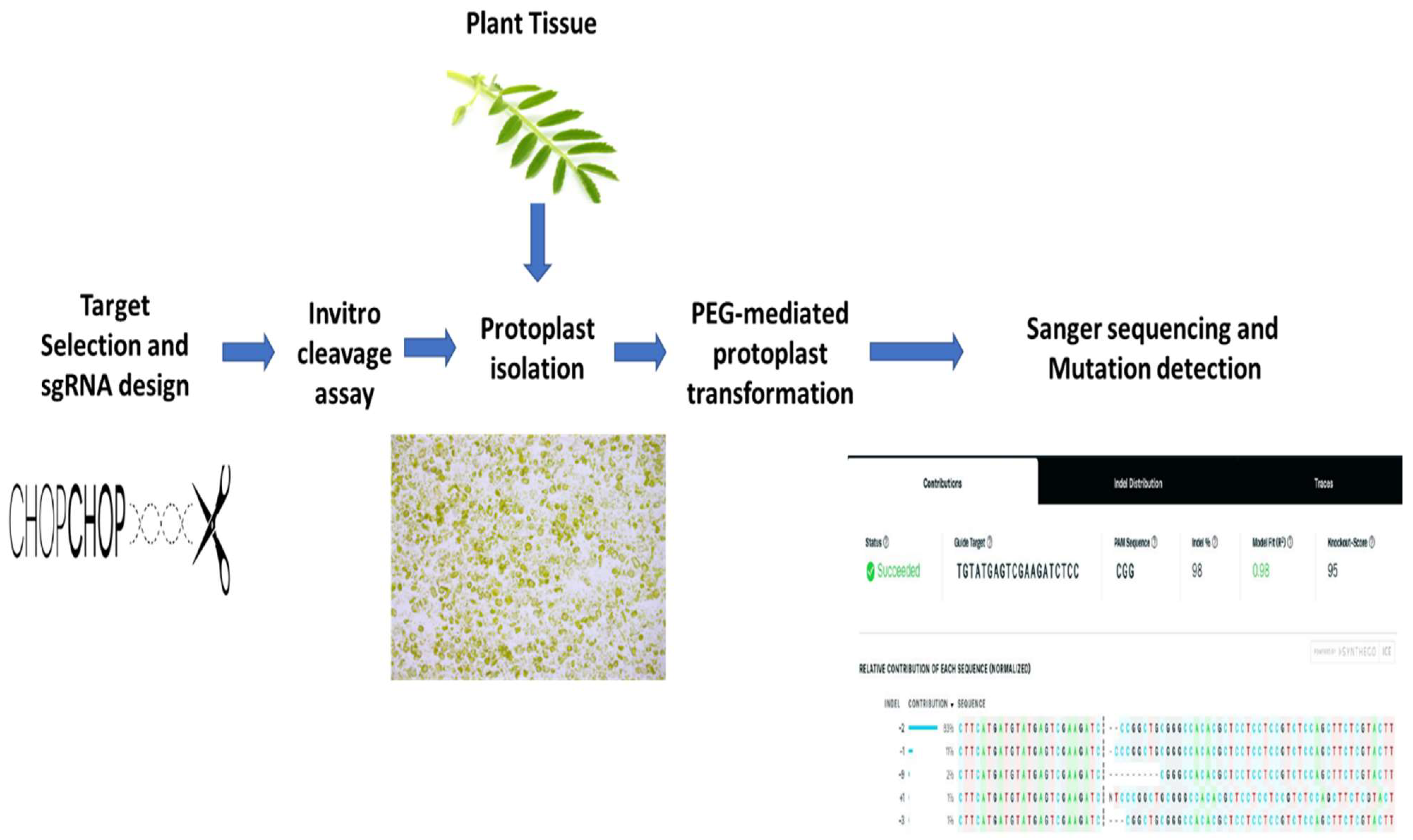
Ijms Free Full Text First Report Of Crispr Cas9 Mediated Dna Free Editing Of 4cl And Rve7 Genes In Chickpea Protoplasts

Male Gamete In Plants Overview Formation Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
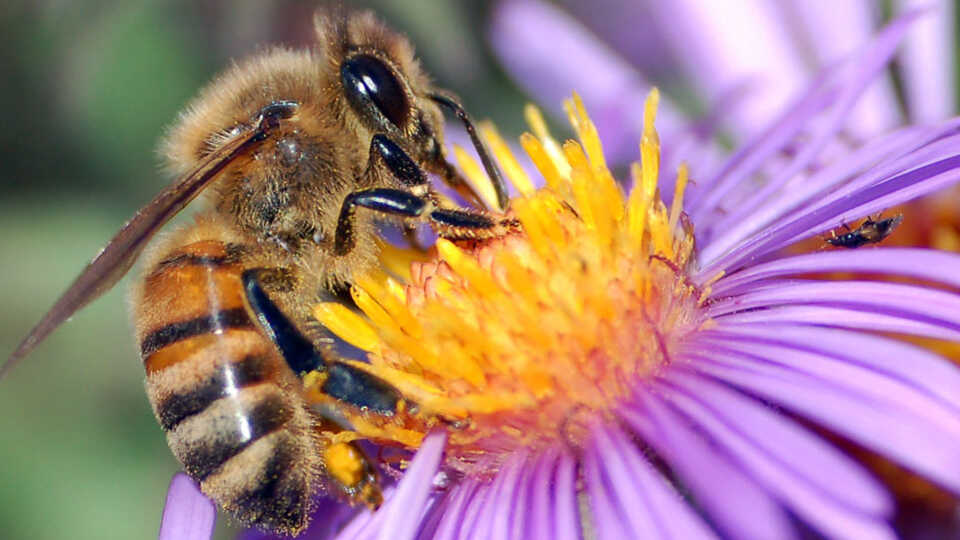

Lesson Plan Flowers Seeking Pollinators

Name The Reproductive Part Of Plant